Renewable energy sources
In the contemporary energy industry, decarbonization has become a global trend, because of ever growing environmental awareness.

In the contemporary energy industry, decarbonization has become a global trend, because of ever growing environmental awareness.

Renewable energy sources (RES) contribute to the improvement of the environment and bring measurable effects in the economy. RES include such energy sources as wind, water, sunlight or biomass, as well as nuclear power in a closed fuel cycle. The largest renewable source available to mankind is solar power. As much as 86 petawatts of power reach the Earth. This is 5000 times more than the current global demand.
Braze plate heat exchangers and JAD-type exchangers operate inside devices using renewable energy sources, such as heat pumps or systems equipped with solar panel collectors.
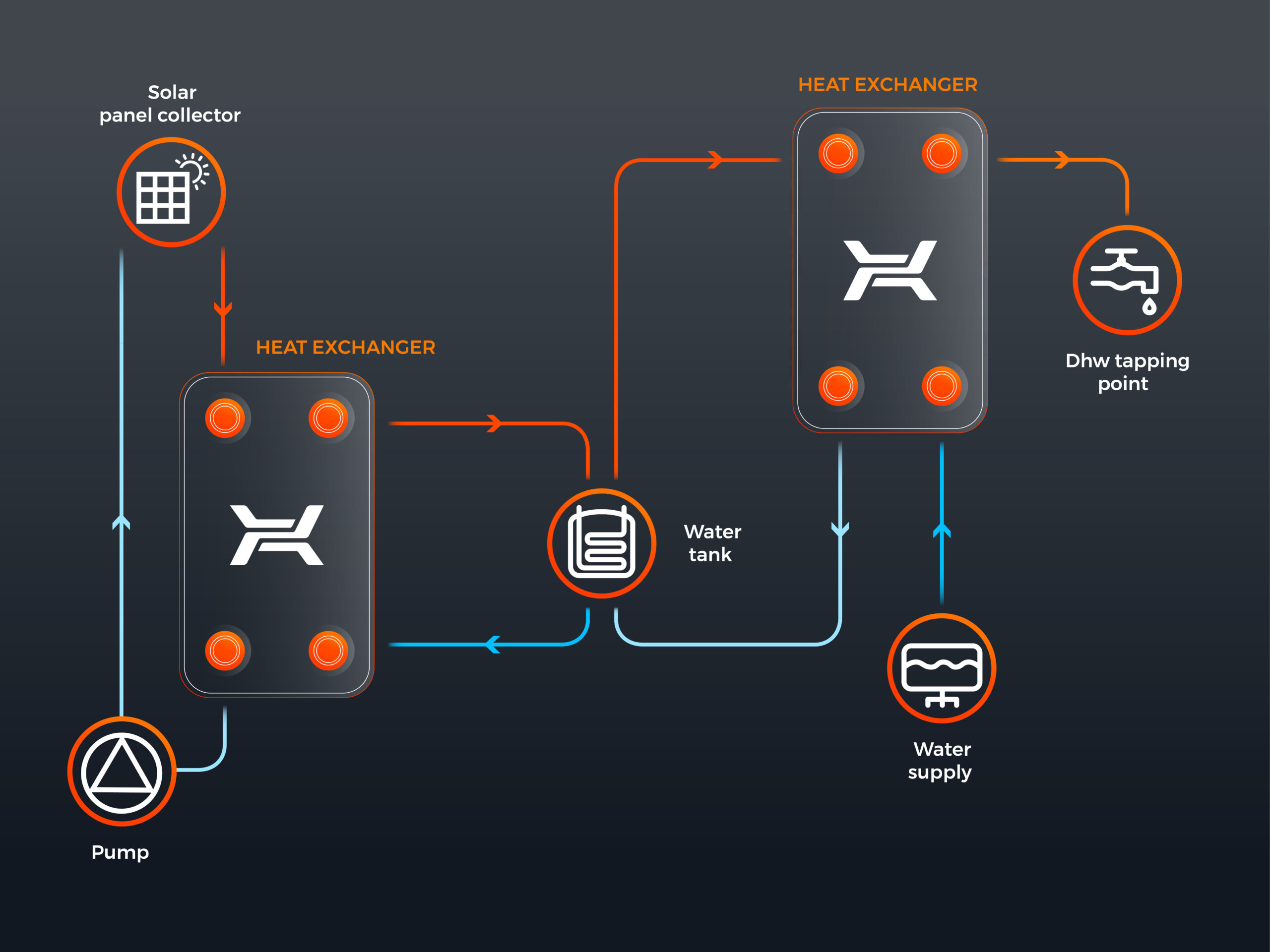
Solar panel collectors, also called photovoltaic collectors, are the most common method of using solar power. The system is made of, for example, solar panel collectors, capacity tanks, heat exchangers and controllers. A solar system is not only a way for heating a house, but also heating domestic hot water.
A solar panel collector absorbs sunlight with an absorber, heating propylene glycol, which becomes a heat carrier. Then a circulating pump pumps the fluid to a heat exchanger inside a tank. The thermal energy is transferred to the water inside the tank. If the sunlight is not enough to heat the water, it is heated up using a conventional heating system.
Modern solar systems operate effectively during any season. Their usage does not lead to emissions of CO2 or harmful flue gases into the atmosphere. The system may also be connected to the existing installation. Investment into a solar system may repay itself within a few years. A user obtains an additional heat source, which does not completely replace the installation, but may significantly reduce costs.
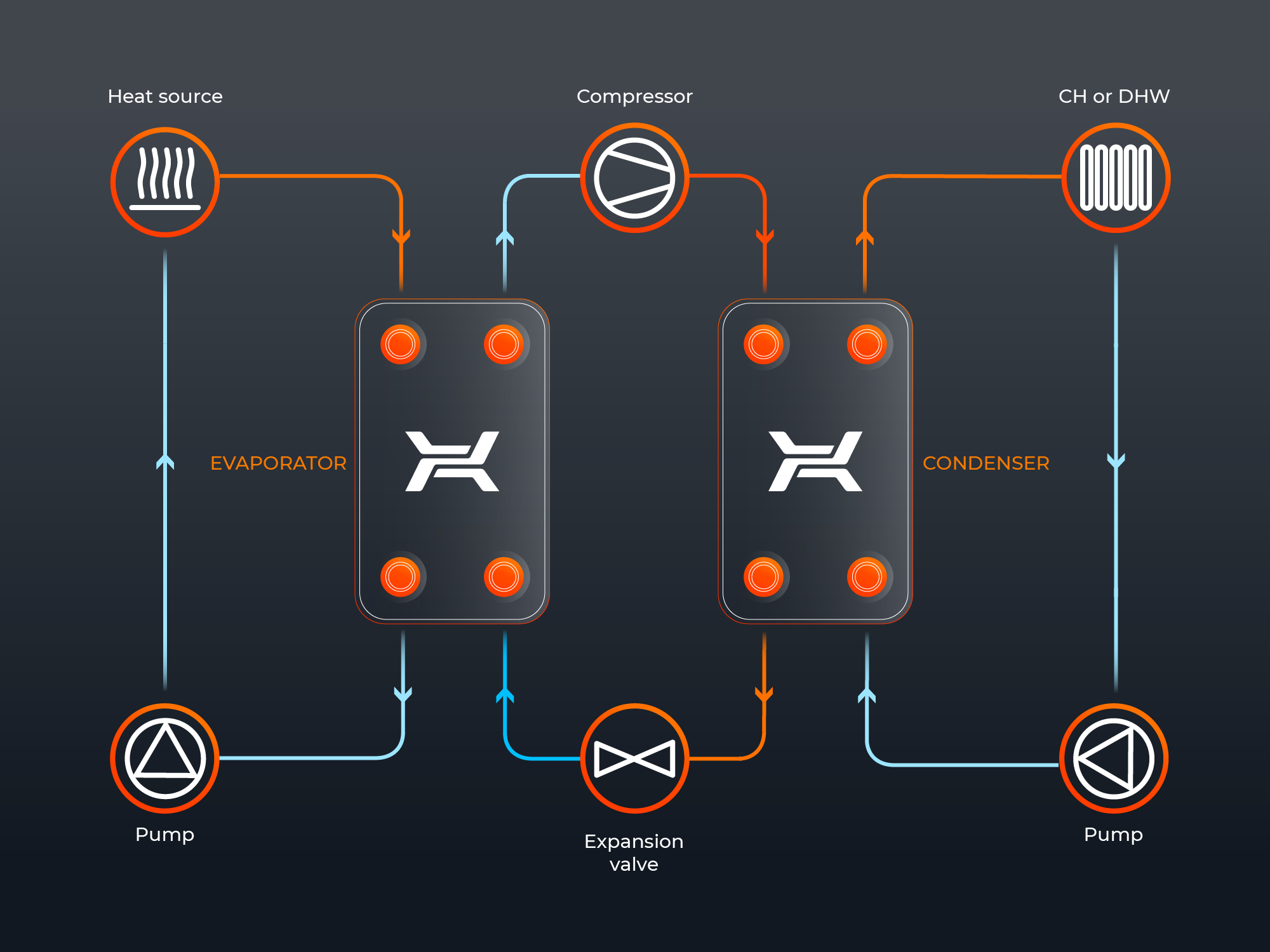
The essentials of heat pump operation consist in using thermal energy collected from the natural environment (lower temperature reservoir) for domestic hot water heating and production (higher-temperature heat reservoir). This process proceeds through the cooling circuit, where the working medium compression and decompression processes occur. An evaporator and a condenser, which are the main elements of the circuit, apart from the compressor and expansion valve, utilize the generated energy in intermediate circuits. The operation of a compressor heat pump may be based on using the natural energy resources provided by the ground, atmospheric air and surface or underground waters.
Heat pumps are ever more often used in modern, energy-efficient construction. They are automated, maintenance-free and economical. An appropriately installed heat pump, ensures significantly lower house heating bills in comparison to the traditional systems and return on the investment will be quick.
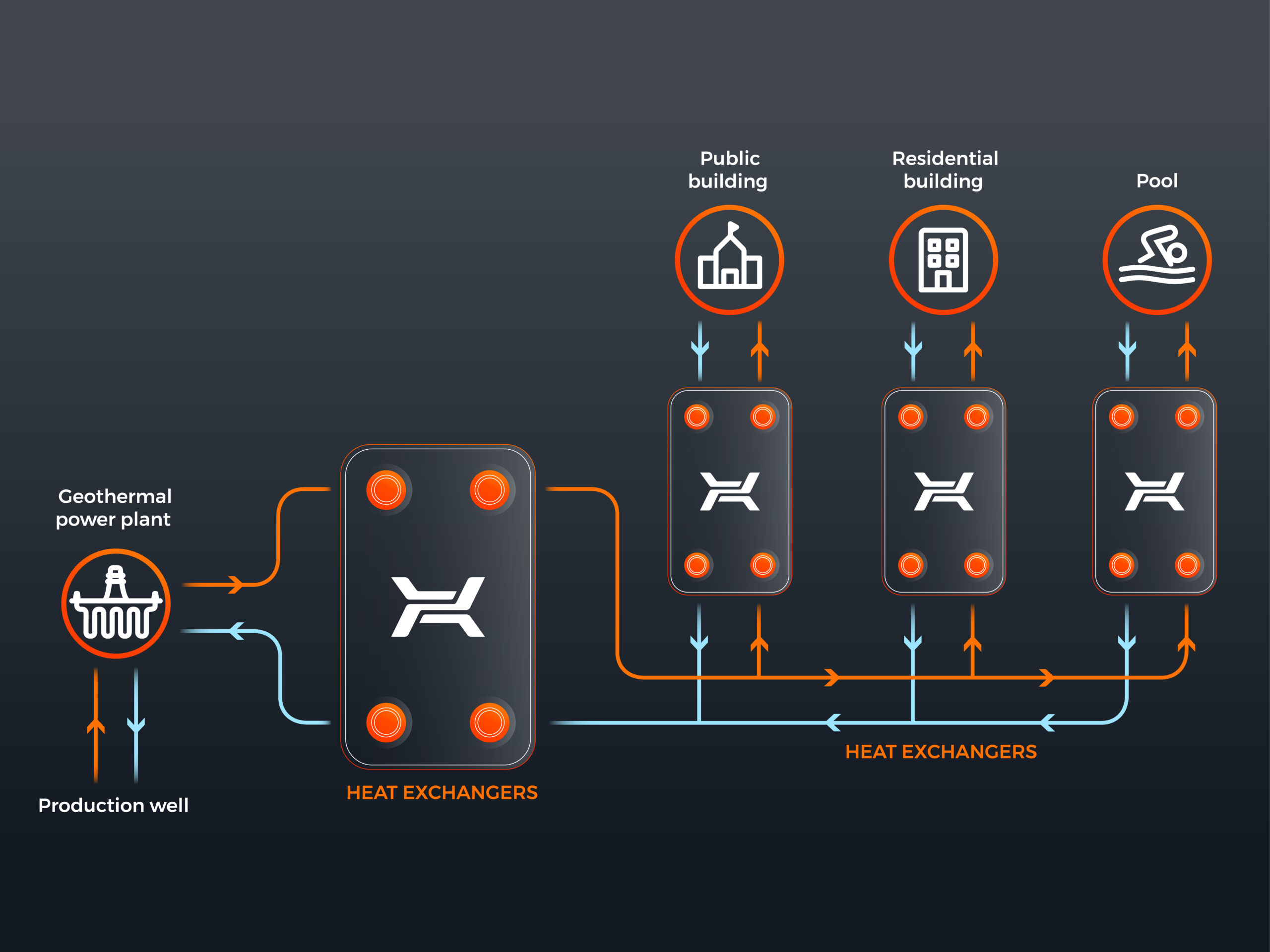
Geothermal energy is one of the renewable energy sources. It comes from rocks, water or soil. It may be collected using ground source heat pumps or deeper water bearing stratums that contain hot water. It is also possible to use the thermal energy of rocks. Cool water is pumped into them and, once heated, hot water is collected. At the depth from 15 to 18 m, the ground temperature is constant through the entire year. When going deeper, the temperature will rise on average by 3°C every 100 meters.
Currently, geothermal energy is used in several dozens of countries. It is the most important energy source in Iceland and the Philippines. A heating and cooling system based on a heat pump is a friendly and economic heating technology.
Ground source heat pumps are devices that may be used for heating rooms, as wells as for domestic hot water preparation and cooling. The ground is artificially regenerated during cooling. Excess heat is evacuated outside of the building and stored in the ground. Heat pump efficiency is increased through active ground regeneration.
Since geothermal waters often contain solid particles and chemicals, it is important to select appropriate heat exchangers. The exchanger must be resistant to aggressive media and offer high performance.
Three basic types of geothermal water energy collection systems are distinguished: